Spectrum Internet is a broadband service provided by Spectrum, offering high-speed internet access. WiFi is a wireless network technology that allows devices to connect to the internet without cables.
Spectrum Internet delivers high-speed, reliable internet service to homes and businesses. It provides various plans to meet different needs, from basic browsing to heavy streaming and gaming. WiFi, on the other hand, uses radio waves to create a local network, allowing devices to connect wirelessly to the internet.
While Spectrum Internet brings the internet into your home, WiFi distributes that connection throughout your space. Understanding the difference helps in optimizing your internet setup for better performance and connectivity. Choosing the right plan and ensuring strong WiFi coverage can greatly enhance your online experience.

Credit: www.spectrum.net
Spectrum Internet Basics
Spectrum Internet is a popular service. It provides fast and reliable internet. Many people use it for work, study, and entertainment. Understanding Spectrum Internet helps make better choices for your home.
Internet Service
Spectrum Internet offers various plans. Each plan caters to different needs. Here is a table showing the basic plans:
| Plan | Speed | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | 100 Mbps | $49.99 |
| Standard | 200 Mbps | $69.99 |
| Premium | 400 Mbps | $89.99 |
Speed And Bandwidth
Speed is how fast data moves. Bandwidth is how much data moves at once. Spectrum Internet offers high-speed options. Here are some key points:
- 100 Mbps is good for light use.
- 200 Mbps is ideal for families.
- 400 Mbps supports multiple devices.
Faster speeds help with streaming and gaming. More bandwidth means less buffering. Choose a plan based on your needs.
Wifi Fundamentals
Understanding the basics of WiFi is essential for anyone using modern technology. WiFi allows you to connect devices without cables. It provides the freedom to move around. Let’s dive into the essential elements of WiFi.
Wireless Networks
Wireless networks use radio waves to connect devices. These devices include smartphones, tablets, and laptops. They connect to the internet without physical cables. WiFi networks can be found at home, in offices, and public places.
A wireless network consists of a few components. These include a router, a modem, and the connected devices. The router sends and receives data over the air. This creates a network that covers a specific area.
Network security is vital. Ensure your WiFi network uses encryption. This prevents unauthorized access.
Router Functionality
The router is the heart of your WiFi network. It connects to your modem and distributes the internet. Routers come with various features. These include speed, range, and security options.
Routers use different frequency bands. The most common are 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Each band has its advantages. The 2.4 GHz band covers a larger area. It is suitable for most home networks. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds. It is ideal for streaming and gaming.
| Feature | 2.4 GHz | 5 GHz |
|---|---|---|
| Range | Larger | Smaller |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Interference | More | Less |
Routers also have security settings. These include firewalls and guest networks. Use these features to protect your network. Keep your firmware updated for the best performance.
How Spectrum Internet Works
Understanding how Spectrum Internet works helps in maximizing your internet experience. Spectrum uses advanced technology to deliver high-speed internet to your home. Let’s break down the process into simple parts.
Cable Infrastructure
Spectrum Internet relies on a robust cable infrastructure. This infrastructure includes a network of cables buried underground or placed on poles. These cables are designed to carry large amounts of data quickly and reliably.
Spectrum uses coaxial cables and sometimes fiber-optic cables. Coaxial cables are common for residential areas. Fiber-optic cables use light to transmit data and are faster but less common in homes.
Modem Role
The modem is a key device in your internet setup. It connects to the cable infrastructure and translates the data for your devices. Without a modem, your devices wouldn’t understand the data signals.
A modem has two main ports: one for the cable and one for your devices. The cable port connects to the incoming cable line. The other port connects to your computer or a WiFi router. This setup ensures your devices receive internet access.
Here is a simple table summarizing the modem’s role:
| Port | Function |
|---|---|
| Cable Port | Receives data from the cable infrastructure |
| Device Port | Transmits data to your devices |
Using a modem bridges your home to the vast internet network. This process is seamless and mostly invisible to users.
How Wifi Operates
Understanding how WiFi operates is crucial for better internet usage. WiFi connects your devices without cables. It uses radio waves for communication.
Signal Transmission
WiFi signal transmission involves sending data through the air. A router sends these signals. Your devices receive these signals using built-in antennas.
The strength of the signal depends on distance and obstacles. Walls and furniture can weaken the signal. Placing your router in a central location helps.
Frequency Bands
WiFi operates on two main frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Each band has its benefits and drawbacks.
| Frequency Band | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4 GHz |
|
|
| 5 GHz |
|
|
Key Differences
Understanding the differences between Spectrum Internet and WiFi is crucial. This knowledge helps you make better decisions for your home network. Below, we’ll explore the key differences. Learn about wired vs wireless connections, range, and mobility.
Wired Vs Wireless
Spectrum Internet often refers to the wired connection coming into your home. This connection uses a coaxial cable or fiber optics. It provides a stable and high-speed internet connection.
WiFi is the wireless network you create using a router. The router distributes the internet signal wirelessly within your home. WiFi allows devices to connect without cables.
| Aspect | Spectrum Internet (Wired) | WiFi (Wireless) |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Wired | Wireless |
| Stability | Very Stable | Can be Unstable |
| Speed | Consistently High | Varies |
| Setup | Requires Cables | No Cables Needed |
Range And Mobility
Wired connections limit the mobility of your devices. You need to stay near the ethernet ports. This can be restrictive for users who move around a lot.
WiFi provides greater mobility. You can connect from anywhere within the router’s range. This makes it ideal for laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
WiFi range can be affected by walls and other obstacles. The signal strength decreases as you move further from the router.
- Wired: Limited mobility, stable connection.
- Wireless (WiFi): High mobility, signal strength varies.
Installation And Setup
Understanding how to set up Spectrum Internet and a WiFi network can save time and effort. Let’s explore the steps involved in both processes.
Spectrum Internet Setup
Setting up Spectrum Internet is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Unbox your Spectrum modem and router.
- Connect the modem to a cable outlet using the provided cable.
- Plug in the modem to a power source and turn it on.
- Wait for the modem to establish a connection (all indicator lights should be solid).
- Connect the router to the modem using an Ethernet cable.
- Plug in the router to a power source and turn it on.
- Wait for the router to establish a connection (indicator lights should be solid).
- Connect your device to the router using an Ethernet cable or WiFi.
Once connected, your Spectrum Internet is ready to use.
Wifi Network Setup
Setting up a WiFi network involves configuring your router to broadcast a wireless signal. Follow these steps:
- Place the router in a central location for optimal coverage.
- Connect the router to a modem using an Ethernet cable.
- Plug the router into a power source and turn it on.
- Access the router’s admin panel via a web browser (usually 192.168.1.1).
- Enter the default username and password (found in the router’s manual).
- Navigate to the wireless settings section.
- Set a network name (SSID) and password for your WiFi network.
- Save the settings and reboot the router.
Your WiFi network is now set up and ready for devices to connect.
Security Considerations
Understanding the security differences between Spectrum Internet and WiFi is crucial. Both have unique security features. This section will help you grasp these differences. You’ll learn about encryption methods and network security tips.
Encryption Methods
Encryption ensures that data sent over the internet remains private. Spectrum Internet uses advanced encryption protocols to protect your data. These protocols include SSL/TLS for secure web browsing. WiFi networks often rely on WPA2 or WPA3 encryption.
Here’s a simple comparison table for clarity:
| Encryption Method | Spectrum Internet | WiFi |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | SSL/TLS | WPA2/WPA3 |
| Web Browsing | SSL/TLS | Depends on Router Settings |
Network Security Tips
To secure your Spectrum Internet and WiFi, follow these network security tips:
- Change default passwords for your router and modem.
- Enable firewalls on your devices.
- Regularly update firmware on your router.
- Use strong, unique passwords for your WiFi network.
- Enable guest networks to isolate devices.
Implementing these tips can significantly enhance your network’s security. Ensure all devices are secure and up-to-date.

Credit: www.spectrum.com
Common Issues And Solutions
Understanding the difference between Spectrum Internet and WiFi can sometimes be confusing. Spectrum Internet is the service that brings the web to your home. WiFi is the technology that distributes the internet wirelessly within your home. Both can have issues. Here, we will explore common problems and their solutions.
Connectivity Problems
Many users face connectivity issues with both Spectrum Internet and WiFi. Spectrum Internet may drop due to service outages or faulty cables. WiFi issues often stem from router placement or interference.
- Spectrum Internet Drops: Check for outages on the Spectrum website. Verify all cables are securely connected.
- WiFi Disconnects: Ensure the router is centrally located. Avoid placing it near other electronics.
- Signal Interference: Use a dual-band router to minimize interference. Keep the router away from thick walls.
Speed Optimization
Speed issues can affect both Spectrum Internet and WiFi performance. Slow speeds may result from network congestion or outdated hardware.
- Check Internet Plan: Make sure your plan meets your speed needs. Upgrade if necessary.
- Update Firmware: Keep your router’s firmware up-to-date. This can enhance performance.
- Reduce Device Load: Limit the number of devices connected to the network. This helps improve speed.
- Use Wired Connection: For critical activities, connect devices directly to the modem. Wired connections are faster and more stable.
By addressing these common issues, you can enjoy a better Spectrum Internet and WiFi experience at home.
Choosing The Right Option
Deciding between Spectrum Internet and WiFi can be tricky. Each offers unique benefits. This section will help you choose the right option.
User Needs Assessment
Understanding your needs is crucial. Do you require high-speed internet for gaming? Or do you need reliable WiFi for your smart home devices?
- High-Speed Internet: Spectrum Internet is great for heavy data usage.
- Smart Home Devices: WiFi is essential for connecting multiple gadgets.
- Remote Work: Reliable internet is a must for video calls and online tasks.
Pros And Cons
Both Spectrum Internet and WiFi have their advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help you make an informed decision.
| Aspect | Spectrum Internet | WiFi |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | High-speed for streaming and gaming | Depends on router quality |
| Reliability | Stable, wired connection | Can be affected by distance and interference |
| Mobility | Limited to wired connections | Wireless, move freely within range |
| Setup | Requires professional installation | Easy to set up with a router |
Evaluate the pros and cons based on your specific needs. Choose the option that aligns best with your usage patterns.
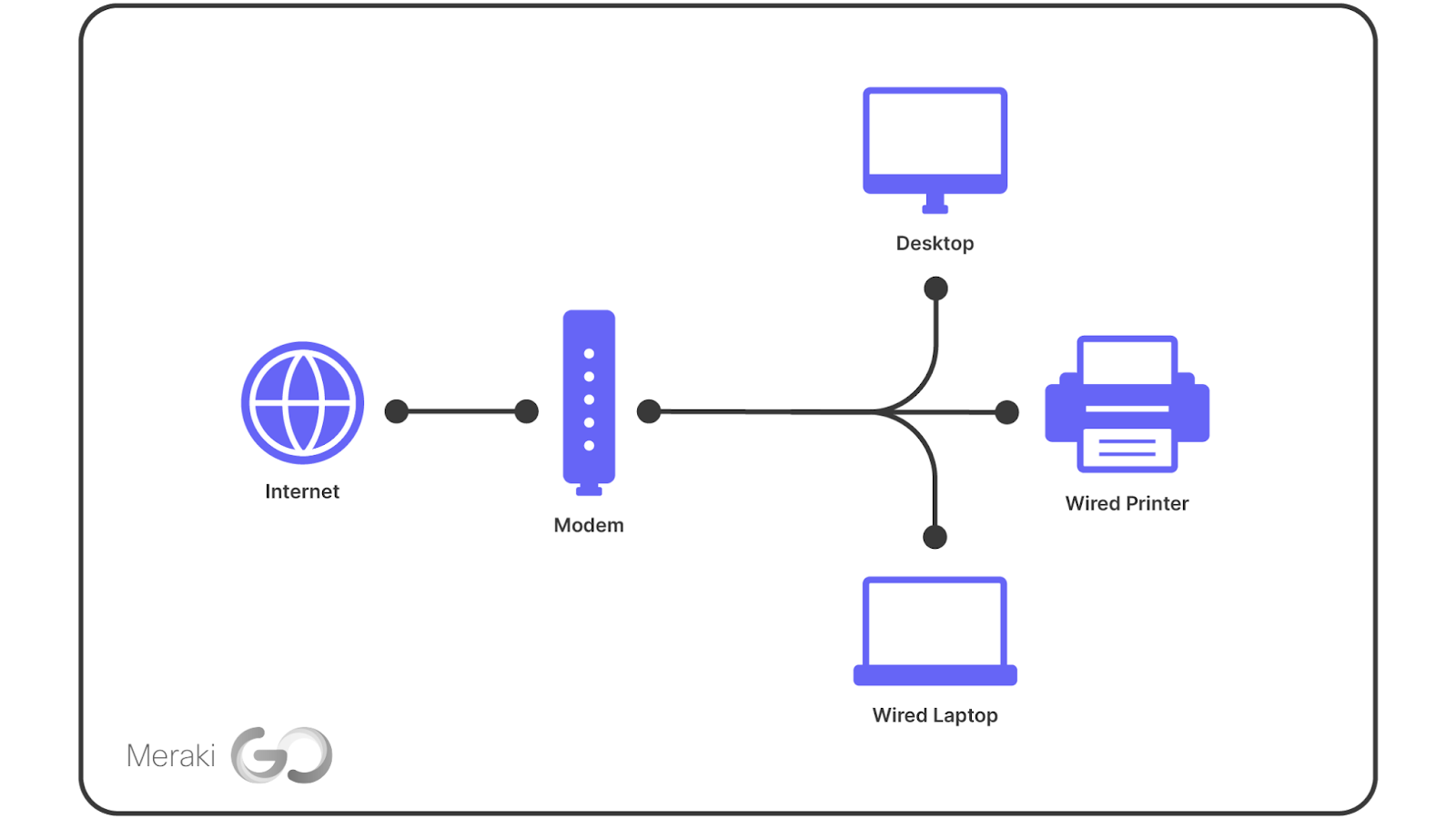
Credit: blog.meraki-go.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Spectrum Internet?
Spectrum Internet is a broadband service provided by Charter Communications. It offers high-speed internet access to homes and businesses. Spectrum Internet packages come with different speeds to suit various needs.
How Does Wifi Differ From Spectrum Internet?
WiFi is a wireless networking technology that connects devices to the internet. Spectrum Internet is the service providing the internet connection. WiFi uses the internet service to allow device connectivity without cables.
Do I Need Spectrum Internet For Wifi?
Yes, you need an internet service like Spectrum Internet to use WiFi. WiFi allows wireless internet access provided by your internet service.
Is Spectrum Internet Faster Than Wifi?
Spectrum Internet speed depends on the package you choose. WiFi speed can be slower due to signal interference. The internet service speed affects the overall WiFi speed.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between Spectrum Internet and WiFi is crucial for optimizing your home network. Spectrum Internet is the service, while WiFi distributes the connection wirelessly. Knowing this distinction helps ensure a smoother online experience. Choose the right setup to maximize your internet performance and enjoy seamless connectivity.
