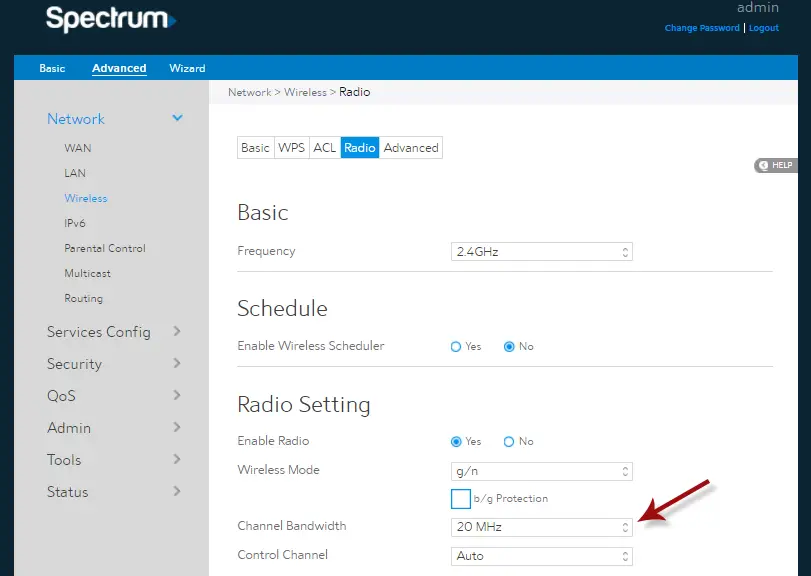
Spectrum change from 5G to 2.4G offers faster data speeds and greater capacity. In the era of advanced connectivity, the transition to the 2.4G spectrum is a significant development.
With an emphasis on high-speed internet access, this change allows for more efficient and seamless wireless communication. By utilizing the 2. 4G spectrum, users can experience improved network performance and better reliability, enhancing their overall online experience. This shift is particularly beneficial for applications that require low latency and high bandwidth, such as video streaming and online gaming.
We will explore the advantages and implications of the spectrum change from 5G to 2. 4G and how it will shape the future of wireless communication.
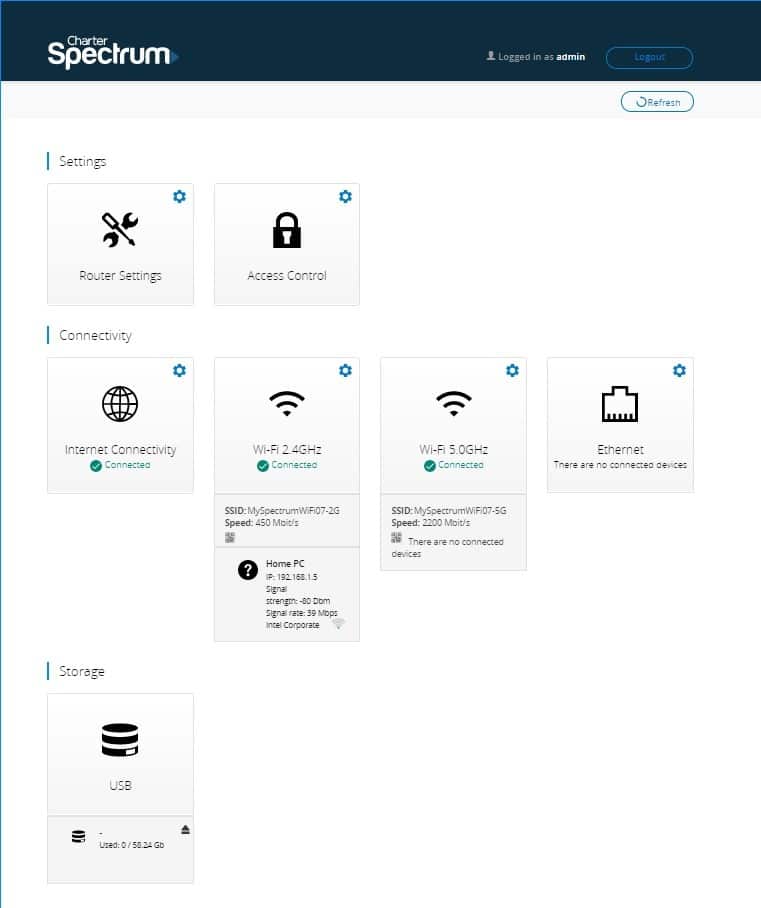
Credit: community.spectrum.net
What Is Spectrum Change?
Spectrum Change refers to the shift from the 5G network frequency to the 2.4G network frequency. This change involves the allocation and utilization of different radio frequency bands for communication purposes. The spectrum, in simple terms, refers to the range of frequencies that wireless signals travel through. It is divided into various bands, and these bands are crucial for wireless communication.
Definition Of Spectrum Change
Spectrum Change, in the context of 5G to 2.4G, is the process of transitioning from utilizing the frequency bands associated with 5G technology to those associated with the 2.4G network. This change impacts the range, speed, and overall performance of wireless communication systems.
Importance Of Spectrum Change
The shift from 5G to 2.4G brings about several important benefits and considerations for wireless communication. Let’s take a closer look at why spectrum change matters:
- Wider Range: The 2.4G frequency band has a wider range compared to higher frequency bands like 5G. This means that devices operating on the 2.4G network can cover larger distances, making it suitable for applications requiring long-range communication.
- Better Penetration: The lower frequency of the 2.4G band allows signals to penetrate obstacles more effectively, such as walls or physical barriers. This makes it ideal for indoor use, where signals need to traverse through walls and reach various devices in the vicinity.
- Compatibility: Many devices, such as smart home appliances, IoT devices, and older Wi-Fi routers, are designed to operate on the 2.4G frequency. By transitioning to the 2.4G network, compatibility is ensured, allowing seamless connectivity between various devices.
- Interference Mitigation: The 2.4G band experiences less interference from other electronic devices compared to higher frequency bands. This leads to improved signal quality and reduced disruptions in wireless communication.
- Established Infrastructure: The 2.4G network has been in use for a longer time and has a more established infrastructure compared to newer technologies like 5G. This ensures better availability and reliability of the network, making it a dependable choice for various applications.
Understanding 5g And 2.4g Spectrum
In the world of wireless communication, there are different spectrums that enable the transmission of data. Two commonly used spectrums are 5G and 2.4G. It’s important to understand the differences between these two spectrums to fully grasp their impact on our daily lives.
What Is 5g Spectrum?
The 5G spectrum refers to the specific range of frequencies allocated for 5th generation wireless networks. These networks operate on higher frequency bands, typically ranging from 30 gigahertz (GHz) to 300 GHz, allowing for faster data transfer rates and lower latency.
With the 5G spectrum, users can experience incredible speeds and connect more devices simultaneously. This spectrum holds great potential for various industries, such as self-driving cars, smart homes, and advanced healthcare systems.
What Is 2.4g Spectrum?
The 2.4G spectrum, on the other hand, operates on a lower frequency band compared to 5G. It operates at around 2.4 gigahertz (GHz), which allows for reliable and longer-range wireless communication.
The 2.4G spectrum has been widely utilized in various devices such as home routers, wireless keyboards, and Bluetooth devices. It provides a good balance between signal strength and distance coverage, making it ideal for household and small office environments.
Differences Between 5g And 2.4g Spectrum
To better understand the differences between 5G and 2.4G spectrum, let’s compare them side by side:
| 5G Spectrum | 2.4G Spectrum |
|---|---|
| Higher frequency (30 GHz – 300 GHz) | Lower frequency (2.4 GHz) |
| Fast data transfer rates and low latency | Reliable and longer-range wireless communication |
| Allows for more connected devices simultaneously | Commonly used in household and small office environments |
The 5G spectrum provides lightning-fast speeds and opens the door to groundbreaking technological advancements. On the other hand, the 2.4G spectrum offers a reliable and wider coverage area, making it suitable for everyday consumer applications.
By understanding the differences between these spectrums, we can appreciate their respective advantages and make informed decisions when selecting devices or services that utilize them.
Reasons For Spectrum Change From 5g To 2.4g
The spectrum change from 5G to 2.4G has several reasons behind it. In this section, we will explore the main factors that have led to this shift.
Interference Issues In 5g Spectrum
One of the primary reasons for the spectrum change from 5G to 2.4G is the interference issues experienced in the 5G spectrum. The higher frequencies used in 5G can be easily obstructed by physical objects such as walls, buildings, and even trees. This leads to reduced signal strength and poorer network performance, especially in indoor environments.
Moreover, the shorter range of 5G signals makes them more susceptible to disruptions caused by electromagnetic interference from other devices. This interference can result in dropped connections and slower data speeds, causing frustration for users.
Compatibility With Existing Devices
Another important consideration in the spectrum change is the compatibility with existing devices. Many consumer devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and smart home devices, already operate in the 2.4G spectrum. By utilizing 2.4G for 5G networks, it becomes easier for users to seamlessly transition to the new technology without the need for expensive hardware upgrades.
This compatibility factor also extends to IoT (Internet of Things) devices, which often rely on the 2.4G spectrum to connect and communicate. By maintaining compatibility, businesses can integrate these devices into their 5G networks effortlessly, enabling the widespread adoption of advanced IoT applications.
Coverage And Range Considerations
Furthermore, coverage and range are important factors when it comes to selecting a frequency spectrum for wireless networks. While 5G offers faster speeds and lower latency, it has limitations in terms of coverage and range. The higher frequencies used in 5G result in shorter wavelengths, which struggle to penetrate obstacles. This makes it challenging to provide seamless coverage in suburban and rural areas.
On the other hand, the 2.4G spectrum has better coverage capabilities due to its longer wavelengths. It can traverse obstacles more easily, allowing for broader coverage in various environments. This makes it an ideal choice for providing reliable connectivity across a wider area, making it more accessible to a larger user base.
Benefits And Challenges Of Spectrum Change
Changing spectrum from 5G to 2. 4G offers both benefits and challenges. It allows for wider coverage and better penetration, but also faces potential interference from other devices operating in the same frequency. Adapting to this shift requires careful planning and management of wireless networks.
Benefits Of Using 2.4g Spectrum
Using the 2.4G spectrum for wireless communication offers several advantages. 1. Increased Range: The 2.4G spectrum has a larger wavelength compared to higher frequency spectrums like 5G, allowing signals to travel further distances. This results in improved coverage, making it suitable for larger areas such as offices, homes, or public spaces. 2. Wide Device Compatibility: Many devices, including smartphones, laptops, wireless speakers, and smart home devices, are designed to operate in the 2.4G spectrum. This compatibility makes it easier for multiple devices to connect to the network without any compatibility issues. 3. Better Penetration of Obstacles: The lower frequency of the 2.4G spectrum enables it to penetrate obstacles like walls and furniture more effectively. This means that Wi-Fi signals can reach different areas of a building, ensuring reliable connectivity throughout. 4. Cost-Effectiveness: Another advantage of using the 2.4G spectrum is its affordability. Wi-Fi routers and devices operating in this spectrum are generally more budget-friendly compared to those that support higher frequency spectrums, making it a cost-effective choice for individuals and businesses. 5. Reduced Interference: Unlike higher frequency bands, the 2.4G spectrum experiences less interference from other wireless devices, resulting in a more stable wireless connection.Challenges Of Transitioning From 5g To 2.4g Spectrum
While transitioning from 5G to 2.4G spectrum offers various benefits, it also poses certain challenges: 1. Decreased Network Speed: One of the main drawbacks of using the 2.4G spectrum is its limited bandwidth, which leads to slower connection speeds compared to higher frequency bands like 5G. This can be a concern for users who require ultra-fast internet speeds for activities like streaming high-definition videos or online gaming. 2. Congestion in Dense Areas: The popularity of the 2.4G spectrum can result in crowded channels, particularly in densely populated areas. With limited available channels, interference can occur, affecting the overall network performance and causing slower speeds and signal dropouts. 3. Interference from Other Devices: The 2.4G spectrum is also susceptible to interference from other devices such as microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors. These common household devices can cause signal interference and impact the quality of the Wi-Fi connection. 4. Limited Number of Non-Overlapping Channels: Compared to higher frequency spectrums, the number of non-overlapping channels in the 2.4G spectrum is limited. This can lead to channel congestion issues and reduced overall network performance in environments where multiple Wi-Fi networks coexist. 5. Reduced Signal Strength at Higher Frequencies: As the frequency increases, the signal strength of the 2.4G spectrum decreases. This means that in certain scenarios where a strong signal is required, such as long-range communication, the 2.4G spectrum may not be the most suitable choice. To maximize the benefits of using the 2.4G spectrum and mitigate the challenges, proper network planning, and management are essential. By considering factors such as channel selection, interference sources, and network congestion, users can optimize their Wi-Fi experience in the 2.4G spectrum.Future Implications Of Spectrum Change
The spectrum change from 5G to 2.4G is expected to have a significant impact on the future of wireless communication. It will affect not only the network expansion of 5G but also bring about technological advances in the 2.4G spectrum. Let’s dive deeper into the implications of this spectrum change.
Impact On 5g Network Expansion
The spectrum change from 5G to 2.4G will have a direct impact on the network expansion of 5G technology. As 2.4G spectrum operates at a lower frequency, it provides better coverage and can penetrate obstacles more effectively compared to higher frequency bands used by 5G. This means that with the spectrum change, 5G networks will be able to reach a wider range of areas, including rural and suburban regions, where high-frequency bands may face limitations.
The lower frequency of the 2.4G spectrum also allows for longer-distance transmission, making it suitable for applications that require wider coverage, such as IoT devices, smart city infrastructure, and industrial automation. This opens up new possibilities for 5G to expand its reach and cater to a broader range of use cases.
Moreover, the spectrum change can help address the issue of signal interference. As the demand for wireless connectivity continues to grow, the available frequency bands become more congested, leading to interference and degraded performance. By utilizing the 2.4G spectrum, 5G networks can alleviate congestion and provide a more reliable and consistent user experience.
Technological Advances In 2.4g Spectrum
The spectrum change from 5G to 2.4G also brings about exciting technological advances within the 2.4G spectrum itself. This frequency band has been widely used for Wi-Fi communication and has benefited from continuous research and development over the years. With the increasing focus on the 2.4G spectrum, we can expect further enhancements and innovations in this domain.
One of the key technological advances is the introduction of Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax. This latest Wi-Fi standard offers higher data transfer speeds, increased capacity, and improved efficiency compared to its predecessors. The spectrum change provides an opportunity for 2.4G-based Wi-Fi networks to adopt Wi-Fi 6 technology, enhancing the overall wireless connectivity experience for users.
Additionally, the 2.4G spectrum enables the deployment of various IoT devices. With its wider coverage and better penetration capabilities, IoT devices can be seamlessly integrated into smart homes, healthcare systems, transportation networks, and more. This proliferation of IoT devices powered by the 2.4G spectrum will drive further advancements in areas such as home automation, remote monitoring, and asset tracking.
In conclusion, the spectrum change from 5G to 2.4G will have profound implications for the future of wireless communication. It will not only impact the expansion of 5G networks by enhancing coverage and addressing interference issues but also unlock technological advances within the 2.4G spectrum itself, enabling the adoption of Wi-Fi 6 and the proliferation of IoT devices. The spectrum change presents an exciting future for wireless connectivity and opens up new doors for innovations in various industries.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Credit: www.spectrum.net
Frequently Asked Questions Of Spectrum Change 5g To 2.4g
What Is The Difference Between 5g And 2.4g?
The main difference between 5G and 2. 4G is the frequency band they operate on. 5G operates on a higher frequency band, allowing for faster speeds but shorter range, while 2. 4G operates on a lower frequency band, offering slower speeds but longer range.
Why Would Someone Change From 5g To 2.4g?
There are several reasons why someone might choose to change from 5G to 2. 4G. One reason could be the need for a longer range, as 2. 4G offers a better signal penetration through walls and other obstacles. Another reason could be the presence of interference, as 2.
4G is less susceptible to interference from other devices.
Can I Use Both 5g And 2.4g At The Same Time?
Yes, most modern devices are capable of using both 5G and 2. 4G simultaneously. This allows for increased compatibility with a wider range of devices and provides flexibility in choosing the best frequency for a particular situation. However, it’s important to note that using both frequencies at the same time may result in some performance trade-offs.
Conclusion
The shift from 5G to 2. 4G in the spectrum has sparked considerable interest in the tech world. With faster speeds and lower latency, 5G seemed like the future. However, the utilization of 2. 4G has its own advantages, including better range and compatibility with a wider array of devices.
As wireless technology continues to evolve, it’s crucial to adapt and embrace these changes. Stay tuned for further developments in the spectrum change.